Allergic Conjunctivitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Bangalore is often referred to as the Allergy Capital of India due to the high prevalence of allergy-related conditions. Many individuals experience a noticeable increase in allergy symptoms upon arriving in the city. One of the most common allergic reactions affecting the eyes is allergic conjunctivitis.
Definition and Overview
Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the conjunctiva, a thin membrane covering the eyes, reacts to allergens by becoming red, itchy, and swollen. This reaction results from an immune system hypersensitivity to substances that are otherwise harmless. Common allergens include pollen, perfumes, air pollution, smoke, pet dander, dust mites, and mould.
Types of Allergic Conjunctivitis
-
Seasonal Allergic Conjunctivitis (SAC) – Triggered by outdoor allergens such as pollen, leading to exacerbations during specific seasons. It is most common during spring and autumn when pollen counts are high.
-
Perennial Allergic Conjunctivitis (PAC) – Caused by indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and mould, resulting in persistent symptoms throughout the year.
-
Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) – A more severe, chronic form primarily affecting young males in warm climates, often associated with intense itching and thick mucous discharge.
-
Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis (AKC) – A rare but serious condition associated with atopic dermatitis, leading to chronic inflammation and potential corneal damage.
-
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis (GPC) – Often caused by prolonged use of contact lenses, resulting in irritation and the formation of large papillae on the inner eyelid.
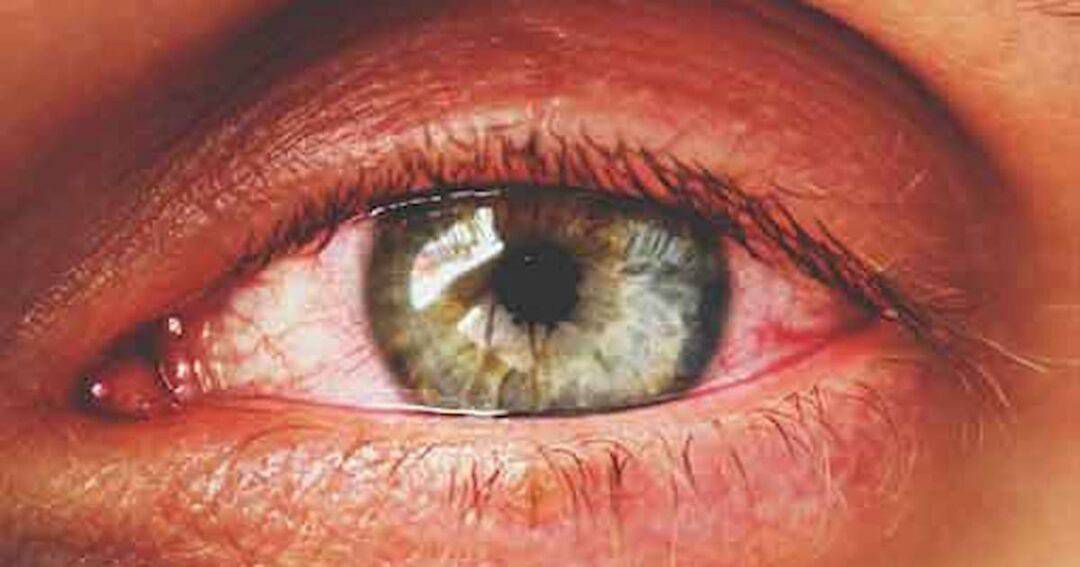
Clinical Manifestations
-
Ocular redness
-
Excessive tearing
-
Eye itching
-
Mucous discharge
-
Eyelid edema (swelling)
-
Sensitivity to light (photophobia) in severe cases
Although allergic conjunctivitis can cause significant discomfort, it is typically a superficial condition that does not impair vision or lead to blindness. However, chronic or severe cases, such as VKC or AKC, may lead to complications affecting vision. Diagnosis is primarily clinical, based on patient history and symptomatology, although allergy testing and conjunctival scrapings may be beneficial in identifying specific triggers.
Management and Preventive Strategies
The most effective approach to managing allergic conjunctivitis is to minimize exposure to allergens. The following measures may help:
-
Utilize allergen-proof mattress and pillow covers.
-
Wash bedding regularly in hot water to eliminate dust mites.
-
Reduce carpeting to limit dust mite accumulation.
-
Maintain a clean indoor environment to mitigate dust and mold.
-
Install high-efficiency air filters and replace them frequently.
-
Keep windows and doors closed to limit outdoor allergen intrusion.
-
Avoid direct exposure to pet dander if allergic.
-
Limit contact lens wear if experiencing persistent symptoms.
Symptomatic Relief and Home Remedies
-
Application of cold compresses to alleviate ocular inflammation.
-
Use of artificial tears or lubricating eye drops to flush out allergens and provide relief from dryness.
-
Avoid rubbing the eyes, as this can exacerbate symptoms and increase irritation.
Pharmacological Interventions
If conservative measures prove insufficient, medical therapy may be necessary. Common treatments include:
-
Antihistamine and decongestant eye drops – Provide symptomatic relief from itching and redness but should be used with caution due to the risk of rebound hyperemia (worsening of redness upon discontinuation).
-
Oral antihistamines – Aid in controlling systemic allergic reactions but may cause ocular dryness.
-
Mast cell stabilizers – Used prophylactically to prevent recurrent allergic episodes; these require regular use for optimal effectiveness.
-
Chilled eye drops – Refrigerated formulations can enhance symptom relief and provide a soothing effect.
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – May help reduce inflammation and discomfort in moderate cases.
Role of Corticosteroids
In refractory cases, ophthalmologists may prescribe corticosteroid eye drops for rapid symptom resolution. However, these agents should be used judiciously under medical supervision due to potential complications such as cataract formation, glaucoma, and secondary infections. Prolonged use should be monitored with regular intraocular pressure checks.
Emerging Treatments
Recent advancements in treatment options include:
-
Immunotherapy (Allergy Shots or Sublingual Tablets) – Can help desensitize the immune system to specific allergens, reducing the severity of allergic reactions over time.
-
Biologic Therapies – New monoclonal antibodies targeting specific inflammatory pathways may offer long-term relief for severe allergic eye conditions.
Conclusion
While allergic conjunctivitis can be a persistent and uncomfortable condition, it can be effectively managed with appropriate preventive and therapeutic measures. Patients experiencing severe, recurrent, or unresponsive symptoms should seek consultation with an ophthalmologist for specialized care and long-term management strategies. With advancements in treatment, those affected can achieve better control over their symptoms and improve their quality of life.