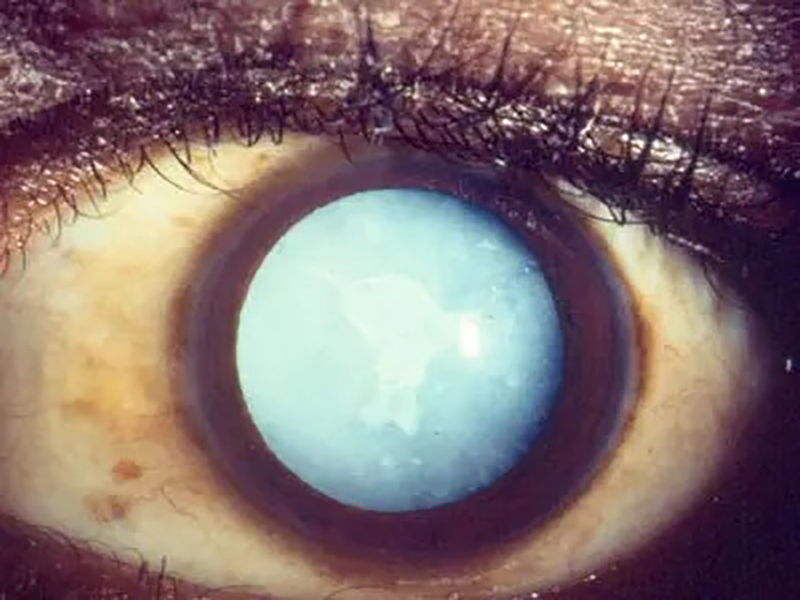
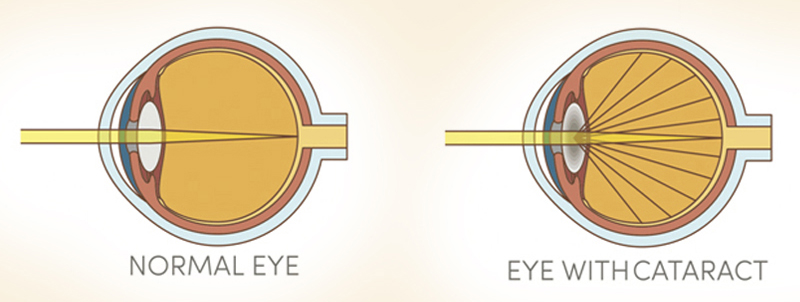
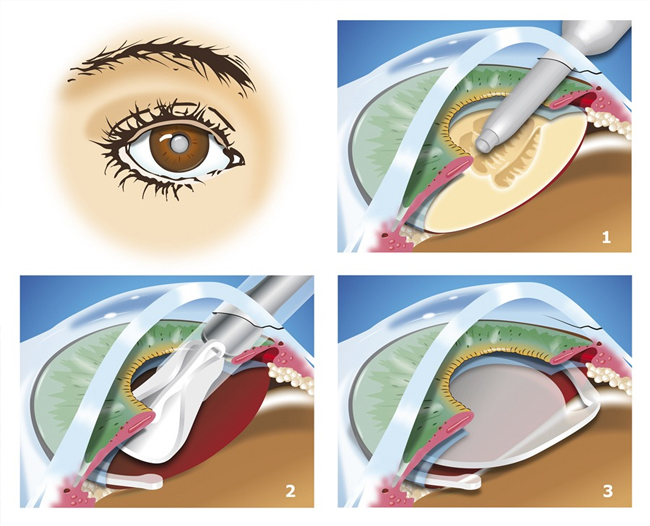
Types of Cataract Surgery
1. Standard Phacoemulsification (Phaco)
-
Performed through a 2.8 to 3.2mm incision.
-
Uses ultrasound waves to break up the cloudy lens, which is then removed through a small incision.
-
A foldable IOL is inserted to replace the natural lens.
-
Quick recovery time and minimal complications.
2. Micro Incision Cataract Surgery (MICS)
-
Most frequently performed procedure.
-
Involves a very small incision of 2 to 2.2mm to remove the cloudy lens
-
Since the incision is very small there is no need for anethesia during surgery & also no need for sutures or Bandage
-
Faster recovery.
Choosing the Right Intraocular Lens (IOL)
During cataract surgery, the cloudy lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL). Several types of IOLs are available:
-
Monofocal IOLs: Provide clear vision at a single distance (near or far); glasses may still be needed.
-
Multifocal IOLs: Allow clear vision at multiple distances, reducing dependence on glasses.
-
Toric IOLs: Correct astigmatism and provide sharper vision.
-
Extended Depth of Focus (EDOF) IOLs: Offer an enhanced range of vision with minimal visual disturbances.
For more details on types of IOLs, please see the section of Types of IOLs & How to choose them.
What to Expect Before, During, and After Surgery
Pre-Operative Instructions for Cataract Surgery
To ensure a successful surgery and smooth recovery, patients should follow these pre-operative instructions:
1. Pre-Surgery Eye Examination
-
Your ophthalmologist will conduct a comprehensive eye exam to determine the severity of your cataract and measure your eye for the correct intraocular lens (IOL).
-
Discuss any existing medical conditions, medications, or allergies with your doctor.
2. Medication Adjustments
-
Some medications, especially blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin, may need to be adjusted before surgery. Consult your doctor for specific instructions. But at Samprathi, we generally don’t stop Blood thinners as we do the Bloodless “Eye drop Surgery”
-
Patients with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels and inform the surgeon of any changes. Ideally Sugar after food should be less than 200mg%.
-
Continue taking prescribed eye drops if recommended by your ophthalmologist.
3. Fasting Guidelines
- Patients are typically advised to have light breakfast before surgery unless specifically mentioned.
4. Hygiene and Personal Care
- Wash your face and eyelids thoroughly before surgery to reduce the risk of infection.
- Do not wear any makeup, lotions, perfumes, or aftershaves on the day of surgery.
- Avoid wearing contact lenses for at least a few days before surgery, as instructed by your doctor.
5. Transportation Arrangements
- Cataract surgery is typically an outpatient procedure, meaning you can go home the same day.
- Arrange for a friend or family member to drive you home, as your vision may be blurry after surgery& you will not be able to drive.
6. Clothing and Accessories
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing on the day of surgery.
- Avoid wearing jewellery, especially around the face and neck.
7. Mental Preparation
- Cataract surgery is a quick and painless procedure, typically lasting about 10 minutes.
- Stay relaxed and follow your doctor’s instructions to ensure a smooth experience.
During Surgery
- The procedure typically takes about 10 minutes per eye.
- Performed under topicalanesthesia, means No injection.
- Your cooperation during the procedure is extremely important
- Patients remain awake but experience no pain.
- If you feel you cannot cooperate or are very anxious, you can ask for Local anaesthesia.
- The cloudy lens is removed, and the IOL is implanted.
After Surgery
- Vision improves within a few days, though some blurriness may persist initially.
- Prescription eye drops are required to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid rubbing the eyes, heavy lifting, and strenuous activities for a few weeks.
- Regular follow-up visits are necessary to monitor healing and ensure the best outcome.
Risks and Complications
Cataract surgery is highly safe, but like any procedure, it carries some risks, including:
- Infection is the most dreaded complication
- Inflammation – Redness of the eyes & watering on & off
- Swelling
- Posterior capsular rupture & inability to implant an IOL
- Retinal detachment (rare)
- Posterior capsule opacification (PCO) – clouding of the lens capsule, which can be treated with laser surgery.
Conclusion
Cataracts are a common age-related condition, but cataract surgery offers a highly effective solution to restore clear vision. Understanding the types of surgery, IOL options, and post-operative care can help patients make informed decisions about their eye health. If you experience symptoms of cataracts, consult an eye specialist to discuss the best treatment plan for you.